The state of online shopping is constantly changing, and it never sits still. Buyers expect quick loading pages, an easy checkout, and the same experience at every device. But stores need to introduce new concepts regularly, test different layouts, and add new tools without worrying too.
A headless system benefits both groups. It disassociates the customer-facing layer from the back end. So, staff at the customer-facing company can work with more speed and flexibility and adjust the performance with no disturbances to the core systems. If this happens, then products and content can now be delivered to any device.
The best thing about this method is that, in this case, each layer can be scaled independently, which improves speed. The end result looks very up-to-date and adaptable.
At the same time, it becomes a solid foundation for any sort of expansion, if any is needed. I have written this article to show you the stages of this method, the reasons for its effectiveness, and the possible ways of implementation in a safe and clear way.
What is Headless Commerce?
With the headless concept, the front store is not a part of the back end. The term headless commerce describes the separation between the visual layer and the data layer, which are two different components communicating through APIs.
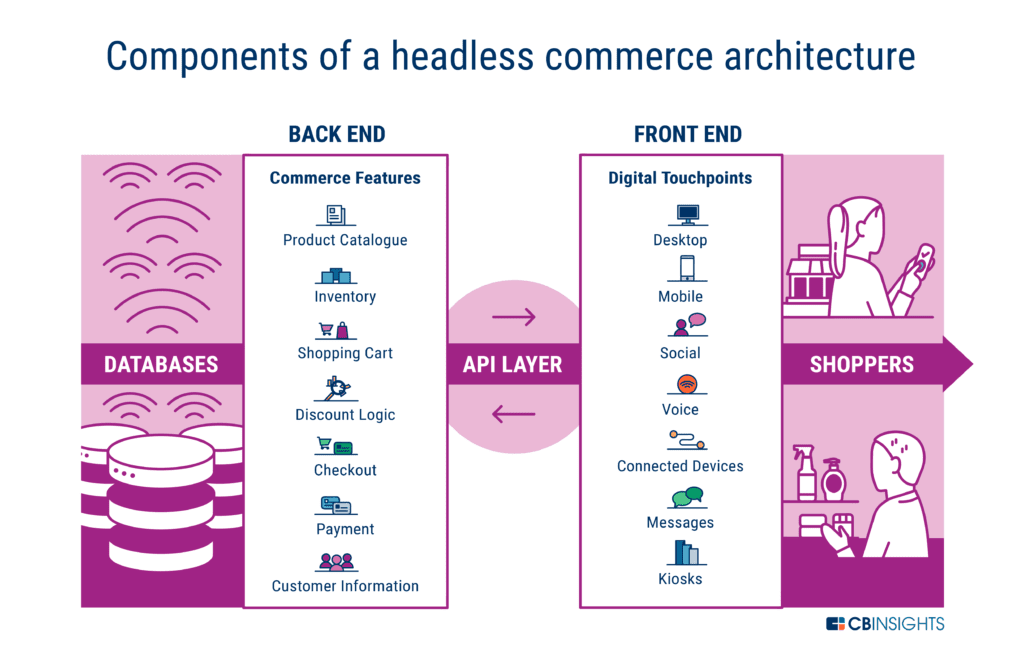
As a result, you can continue to offer tailored experiences on the front with the back taking care of products, orders, and customer data. The notion is straightforward, yet it opens up a plethora of possibilities.
The core parts
- A front end that renders pages, apps, or screens
- A commerce engine for catalog, cart, pricing, orders, and taxes
- A content system for pages, blogs, guides, and media
- A search and merch layer for findability and rules
- A checkout and payment service
- A set of APIs that connect everything
Why Flexibility Improves with a Headless Approach
The separation of the front end enables the designers and developers to implement their changes without having any impact on the checkout process. Content can be published by the marketing teams without being reliant on release cycles. Implemented lessons from the tests will be brought to the live site quickly.
Moreover, you can use the same product data to enter new channels such as mobile apps or kiosks. This is an approach that accommodates various teams and different team sizes.
How Flexibility Shows up in Daily Work
- You can use different front-end frameworks to build different interfaces
- You can reduce the risk of switching a tool by one API contract maintenance
- You can do A/B testing more frequently to test new layouts and copy
- One place to manage web, app, and email content campaigns
- You can use the core rules to enter new regions
How Headless Boosts Performance
Every buyer’s experience step speed is crucial. Tuning each part for speed is possible with headless. To have a fast first paint, the front can use static generation or server-side rendering. The back can scale on its own without affecting the front.
Edge caching minimizes the distance to the user. In addition, you can prefetch data, lazy load assets, and compress images for every device. These little actions combine to a fast and seamless experience.
Practical gains you can expect
- Assets and HTML are prebuilt and cached, which results in faster page loads
- When the server renders near the user, there is a lower time to first byte
- By using code splitting, browsing on mobile becomes smoother
- Because the traffic spreads across layers, you can have more stable peaks during campaigns
- If you concentrate on render and payload size, your Core Web Vitals will be better
Architecture at a Glance
Imagine the stack as a suite of services that interact with each other.
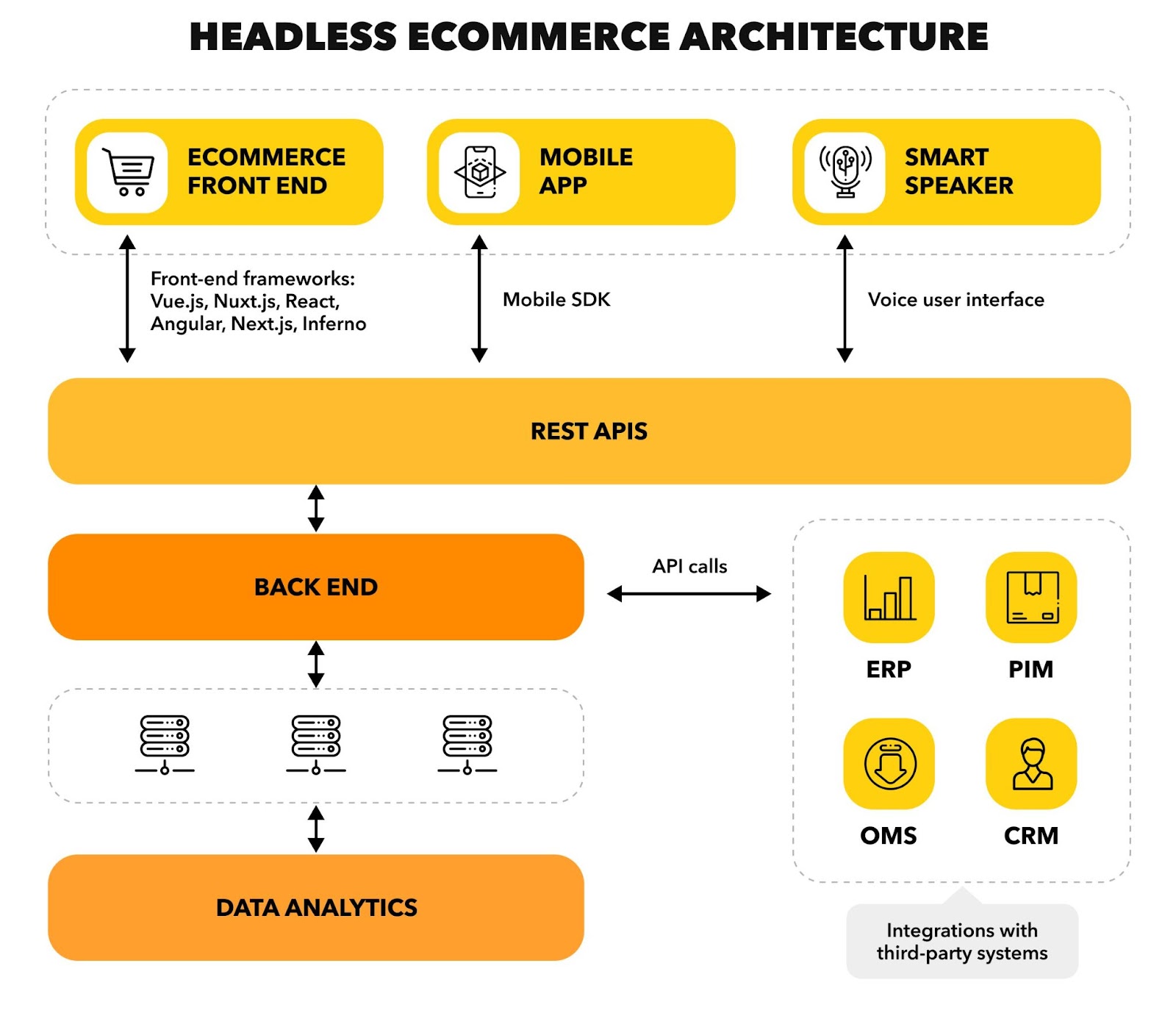
- Presentation layer: A web or native app, a kiosk screen
- API gateway: A single point of entry that routes traffic to services
- Commerce services: Catalog, pricing, inventory, cart, promotions
- Content service: Pages, posts, reusable blocks, and media
- Search and recommendations: Results, filters, rankings, and rules
- Checkout and payments: Address, tax, shipping, cards, wallets
- Analytics and events: Tracking, attribution, and insights
- Identity and access: Sessions, roles, and permissions
Front-End Options
Your front end can be a dynamic app or a static site, or a mix. Many teams use server-side rendering for the first load and client hydration for later moves. Others prebuild pages and fetch data on demand. Choose the method that fits your page types, catalog size, and traffic pattern. Keep code small and simple for speed.
Tips for a lean front end
- Keep components small and focused
- Avoid heavy client logic when a server render is enough
- Use image formats that compress well
- Bundle only what a page needs and load the rest later
- Cache API calls and reuse data across views
APIs and Microservices
APIs are the means of communication. A carefully designed API makes modifying easier and more secure. Begin with unambiguous contracts for entities, prices, shopping cart, and orders.
Implement versioning so that you may add new attributes without affecting the clients. Use rate limiting to safeguard the back-end services. Record each call with trace IDs so troubleshooting becomes easier. In case you have divided your system into microservices, then make sure the scopes are small and managed by a single team.
API design basics that help
- Naming resources with nouns and actions with verbs is the API way of doing.
- One way to increase consistency in API responses is to keep them in the same shape.
- Adding pagination and filters to a catalog query is always a good idea.
- Presenting errors with understandable codes and user-friendly messages is a good practice.
- Keeping documentation, code, and examples closer helps with the documentation of endpoints.
Content Modeling for Headless Websites
Content is the main factor that brings in visitors and retains them. When content is separated from presentation, it is modeled in such a way that it can be reused not only on pages but also on different channels.
Some examples are product guides, stories, FAQs, and comparison blocks. Editors can combine and separate fields if they are kept detailed. This also helps SEO because pages can be relevant and rich without being heavy.
Good patterns for content modeling
- The first step in content modeling is creating small blocks such as hero, feature grid, and callout.
- Every SEO title and meta description gets its field when added.
- Creating and keeping the URL using slugs makes it easy to be read.
- Not only colors, but spacing and character design tokens that are different from content.
- Design through localization and regional rules
Checkout and Payment Flows
Checkout is where slow pages hurt the most. Keep the flow short and clear. Use address lookup, auto fill, and wallet payments where it makes sense.
Reduce steps for return buyers by saving preferences with consent. Show clear errors in line. Make sure taxes and shipping update in real time so costs never surprise the buyer.
Things that speed up checkout
- One-page checkout or a clear two-step flow
- Wallets like card on file, UPI, or local options by region
- Strong validation rules that do not block the user
- Address hints and suggestions to cut typing
- Real-time stock checks to avoid cart fails
Search and Merchandising
Search helps buyers find what they need. A strong search layer supports synonyms, spell fixes, and filters. Merch rules let you boost items during promos or hide out-of-stock lines.
Tie the index to product data so it updates fast. Track zero result queries and add content or products to fill gaps.
Simple ways to improve discovery
- Show popular queries and related searches
- Use filters that match how people think, like size and fit
- Rank by relevance and fresh stock
- Add badges for new, trending, or limited items
- Blend content results with products when it helps
Personalization Without the Creep Factor
Personalization should feel helpful, not pushy. Start with basics like remembering size or favorite categories.

Use on-site behavior to suggest items. Keep data use clear and give easy controls. Lean on session data first, then known preferences with consent. Avoid using sensitive signals.
Tactics that work well
- Recent views and quick access to saved lists
- Simple rules such as showing similar items to those viewed
- Context-aware banners for returns or shipping updates
- Location-aware stock and delivery times with consent
- Email and app messages that match on-site behavior
Omnichannel Experiences
A headless model lets you reuse data and content across many touchpoints. The same product and price can show on the site, the app, a kiosk, or even a store screen.
You can sync carts and wishlists across devices. You can also send confirmation and alerts through email or push with the same design blocks.
Common Patterns
- Start on mobile, finish on desktop, without losing cart
- Scan a code in store to view size and stock
- Use the same content blocks for web and app pages
- Share profiles and preferences across channels with consent
- Offer pickup, ship from store, and returns with a single view
Caching and CDNs
Caching is the fastest way to speed up a site. Use a content delivery network to put pages and assets near users. Cache HTML for routes that do not change often.
Use stale while revalidate so users get a fast page while the cache refreshes in the background. In APIs, cache read-heavy calls like product lists.
Smart Cache Tips
- Set cache keys that include the device or locale where needed
- Purge on content or price updates with webhooks
- Control TTLs by page type, like longer for blogs and shorter for product pages
- Use ETags or last modified for conditional requests
- Monitor hit ratio and fix misses
Edge Compute
Some logic can run near the user. Edge functions can handle redirects, A/B test splits, or simple personalization.
They can also stitch data from more than one API before sending the page. Keep edge code small and fast. Use it for logic that benefits from low latency.
Good use Cases
- Geo routing and local currency hints
- Cookie-based test buckets
- Header rewrites and quick security checks
- Simple recommendations that need a fast read
Progressive Web Apps
A PWA gives app-like speed in the browser. With a service worker, you can cache assets and routes for repeat visits.
Add to home screen can help retention. Use safe fallbacks when a feature is not present. Keep the bundle light so the first load is fast.
PWA Features to Consider
- Offline access for basic browsing
- Install prompts with clear value
- Push notifications with opt-in and value
- Background sync for carts or orders
- Prefetch routes for likely next clicks
Accessibility as a Speed and Reach Win
Accessible pages are easier to use for everyone. Use semantic HTML, clear focus states, and high contrast. Test with keyboard only.
Provide text for icons and images. Announce dynamic content to screen readers. Keep motion optional. Many accessibility steps also help SEO and performance.
Quick Checks
- Headings in a logical order
- Labels and instructions for inputs
- Error states that are clear and polite
- Visible focus for interactive elements
- Sufficient color contrast
Security and Privacy
Security is a shared job. Protect APIs with auth and rate limits. Store secrets in a safe place. Encrypt data in transit and at rest. Keep third-party scripts in check. Review data flows and remove what you do not need. Honor regional privacy rules and give people control of their data.
Basics to Enforce
- TLS for every call
- Strong session handling and rotation
- Least privilege access for services and staff
- Audit logs for sensitive actions
- Regular dependency updates and scans
Costs and ROI
Headless can save money over time, yet it needs planning. You might spend more at the start to set up the stack and train the team.
You then gain from faster changes, better conversion, and less lock-in. Track the value of speed and the lift from tests. Use clear goals so the business can see progress.
Ways to Manage Costs
- Start with a small scope and expand after wins
- Reuse components and content blocks across brands or regions
- Choose managed services where it saves time
- Automate deploys, tests, and rollbacks
- Watch cloud and CDN usage and tune often
Build or Buy
You can assemble the stack with managed services or build more in-house. Managed parts speed up launch and reduce ops work.
Custom parts give control where it matters, like the front end or search rules. Many teams mix both. Decide by looking at time to value, skills on the team, and the need for change in the future.
A Simple Decision Frame
- Ask if the feature gives an edge. If yes, build. If not, buy
- Check if the team can own it for years
- Compare total cost, not just license or cloud bills
- Look for exit paths if needs change later
- Favor tools with open APIs and strong docs
Migration Roadmap
Safe moving is always linked to a good plan. No need to change all at once. First, set a pilot. Know, then enlarge.
Step by Step
- Map your systems, data, and pain points
- Establish goals and metrics of success, both technical and business
- Choose a pilot area, for instance, like a content hub or one region
- Lay out the content model and API contracts
- Get the front end for the pilot and connect with actual data
- Implement analytics, logging, and alerts
- Test performance and fix gaps
- Prepare editors and support teams
- Introduce the pilot behind a flag
- Evaluate the performance and prepare the next slice
Data, Analytics, and Attribution
Data is the source of knowledge. In a headless stack, there are events all over. Use a shared schema for basic actions like view, add to cart, checkout, and purchase.
Send events with the same IDs so that you can connect them. Obey privacy settings. Build speed, funnel steps, and revenue dashboards. Check trends frequently and respond to them.
Events to Define Well
- Page and screen views with route and referrer
- Product list and detail views with IDs and positions
- Search queries and filter use
- Cart adds and removals
- Check out steps, payments, and order status
Work with ResultFirst
The success of headless is based on clear steps and gradual wins. ResultFirst can be your practical support if you are looking for a hand to plan and deliver a safe rollout. Furthermore, our eCommerce SEO services ensure your headless store achieves optimal search visibility, enhanced performance, and measurable business outcomes.
What you Get
- A quick audit of your store, stack, and goals
- A pilot plan that fits your budget and timeline
- A content model and API blueprint that scales
- A performance playbook with targets for Core Web Vitals
- A migration map with clear owners and checkpoints
- Training for editors and a support handoff
Conclusion
With this concept being used instead of other choices, stores become light and fast. The teams can implement changes with less risk, and most importantly, customers get simple pages and fast checkout. The method works for a lot of sizes and markets. You can start small, see the results in the data, and slowly increase the stack.
Do not forget to keep content clean, code simple, and pages quick. Measure and adapt carefully. If you smartly plan your move, you will get the benefits without chaos.
If you want help to make the way and keep from stumbling along the way, ResultFirst is a great partner. Most important is the focus on buyer value and the habit of steady improvement across your site and app.
WHAT TO READ NEXT
READY TO BUILD PREDICTABLE ORGANIC GROWTH?
We are the only TOP SEO services agency providing Real Results in a Real Performance model. We help growth hungry companies outperform their competition and achieve 300%+ growth in their digital marketing initiatives.
- San Jose, CA, 95120
- +1-888-512-1890
- sales@resultfirst.com
















